
BILLIONS AGAINST BAYER
Mobay: Monsanto & Bayer’s 1954 Hook-up
By Alexis Baden-Mayer, Organic Consumers Association:
Bayer bought Monsanto and retired its infamous name in 2018.
But did you know that they had merged before?
After World War II. In a company called Mobay.
What would a patriotic American company like Monsanto, an essential part of the top secret Manhattan Project, be doing with Bayer, a company that did most of its business during the war at Auschwitz?
The answer lies in Monsanto’s participation in Operation Paperclip, the infamous CIA ratline that funneled thousands of Nazi scientists into the U.S. government and American companies, at a time when displaced Jews, fresh from the death camps, weren’t being welcomed into the U.S.
In service of Hitler’s war machine, Bayer and its parent company I.G. Farben made huge investments in scientific breakthroughs that Monsanto was desperate to get its hands on—no matter that the expertise had been achieved using imprisoned Jews as slaves and test subjects.
Nuremberg’s prosecutor didn’t think I.G. Farben/Bayer just took advantage of Hitler’s Holocaust. He called it the “Machiavellian planner.”
(Not that Monsanto was a paragon of virtue, having just served as an accomplice in the murder of hundreds of thousands of Japanese civilians in Hiroshima & Nagasaki.)
Monsanto and Bayer’s work together as Mobay (and ever since) is exactly what one would expect from the merger of a Nazi collaborator and a Pentagon contractor.
They made Agent Orange for the Vietnam War.
Then, they brought some of the same toxins into the food system through genetically engineered crops.
Now, they’re ushering in an era of synthetic Frankenfoods, true to Bayer’s Nazi roots. (The sailors on Nazi U-boats subsisted on “butter” made from coal!)
It was during the Mobay years that Monsanto worked with the military and the CIA on experiments using unwitting human subjects—everything from radiation exposure to brain surgery for mind-control—often alongside Nazi scientists brought to the U.S. through Operation Paperclip.

MONSANTO MAKES US SICK
Mexico Defends Their Corn, Saying No to GMOs as Glyphosate’s Association with Cancer Burgeons
Ernesto Hernández-López writes for Common Dreams:
“So-called “Free trade” promises lower prices and more supply, but it derails food security.
Mexico has been fighting this since the United States began a dispute over genetically modified (GMO) corn. In November, a trade panel made initial filings public. They reveal that the U.S. plays for agribusiness, which includes chemical and biotech companies.
Meanwhile, by banning GMO corn, Mexico secures supplies of an important daily staple and limits cancer risks from glyphosate. American positions appear oblivious to this.
This involves Mexico’s Decree, announced in February. It bans GMO corn for human consumption, limited to corn in tortillas or masa (dough). In August, the U.S. invoked a panel under NAFTA 2.0, formally called the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA). Showing its hand, the U.S. is out to lunch on various fronts.
Glyphosate’s association with cancer grows like a weed. A few weeks ago, a Missouri jury ordered its maker, Bayer Monsanto, to pay $1.56 billion, finding the chemical caused lymphoma cancer. This dealt the agribusiness giant its fourth straight loss.”
Also read “Glyphosate: Cancer and Other Health Concerns” by Stacy Malkan

NATURAL HEALTH
Fermentation 101 — How to Get Started with DIY Probiotics
Kris Bordessa writes for Attainable Sustainable:
Are you ready to dive into fermentation? It’s an easy way to preserve fresh produce, but the process can sound a bit intimidating (it’s not!). What is fermentation?
Fermentation is the process used to create beer and wine. That’s often what people think of when they hear the word. Those beverages are produced with yeast, though, as is this strawberry mead.
Lacto-fermentation is the process used when we make fermented vegetables, fruits, and even kombucha. Lactobacillus bacteria converts sugars into lactic acid. This good bacteria inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria. The lactobacillus organisms that develop when we ferment food preserves it, but it’s also a boon to our digestive tract. Foods fermented in this way provide us with the probiotics that we’ve heard so much about in recent years.
Two fermentation methods:
When fermenting foods, you’ll choose between a brine method and direct salting.
The brine method calls for covering fresh vegetables with a mixture of salt and water. This is most commonly used with whole vegetables or those cut into chunks. Fermented nasturtium seeds and sugar snap peas are an example of this process.

ENVIRONMENT & CLIMATE
Regeneration Is Life, an Agroecological Paradigm To Overtake the Climate Crisis
Navdanya International writes:
“There are two main paradigms of thinking of ourselves in the world and of our relationship with the Earth. We either think of ourselves as being separate from Nature or as being one and part of it. The industrial agriculture paradigm, which sees the world as a machine, has created devastation on the planet.
Fossil fuels, the lifeblood of the industrial paradigm, are used in almost every phase of the food chain from fossil-fuel-based pesticides or synthetic fertilizers, gas-guzzling farm equipment, and a fossil-fuel-based global processing, packaging, and transport system. The fertilizer industry is responsible for more than a fifth of total estimated greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture systems worldwide. Representing 2.4% of total worldwide emissions, of which 60% are generated after the products are applied to soils.
Glyphosate, one of the most commonly sprayed pesticides, has caused the mass extinction of biodiversity, and is linked to a range of detrimental health effects. Around 44% of farmers are poisoned by pesticides every year, equalling around 20,000 deaths annually. Monsanto, the creator of glyphosate, has been sued for over $2.42 billion USD for having caused cancer to thousands of victims.”
TAKE ACTION: Tell Your Lawmakers to Restrict Risky mRNA Foods!

SUPPORT OCA
Make the World More Just, Healthy and Happy for All
All of us at OCA want to thank you for your loyalty, support, and engagement over the past tumultuous year. Greetings and best wishes for a new year filled with hope, love and strength as we move forward together to make the world more just, healthy and happy for all.
Since Ronnie passed in April we have felt your steadfast support and continued belief in our work, we are asking you at this important time to again support us with a donation if you are able. The issues we are working on are more important than ever in the face of so much uncertainty in the world.
More and more people understand that organic, regenerative, and healthy food is the best medicine, complemented with natural health practices; while chemical-intensive, energy-intensive, genetically engineered food, industrial farming, and overuse of pharmaceuticals are literally killing us and the planet.
Over the next year we will continue our decades-long campaign to educate and mobilize the public. As always we will expose the bad, how our deteriorating public health and chronic disease epidemic is directly related to our degenerative food, farming, and destructive land use practices—while highlighting the good—how organic and local food, regenerative farming, and natural health practices can resolve our health, environmental, and climate crisis.
Signs of enlightenment, resistance and renewal are emerging all over in the US and worldwide. We promise you on behalf of the OCA and all of our allies and supporters: we’re not only going to get through these disturbing times, we are going to build a new organic and regenerative future on the ruins of the old.
We need your financial support to carry on the struggle. We need your support to build up our positive and regenerative solutions, in the US and worldwide.
Together we will move forward to make 2024 a year for stronger Organics, and Regeneration with a goal of Planting Peace and making a healthier world.
Between now and the end of January, we have a donor that has pledged to double match your donations!
Make a tax-deductible donation to Organic Consumers Association, a 501(c)(3) nonprofit
Make a tax-deductible donation to Regeneration International, our international sister organization
Order your OCA “Planting Peace” bumper stickers from our Minnesota office

SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY
Food for People, Not Factory Farms or Frankenfood Factories!
Alexis Baden-Mayer, Political Director at Organic Consumers Association reports:
Biotech companies like Bayer say synthetic protein is going to save the planet.
You might believe that, especially if you think corn ethanol is more environmentally friendly than gasoline.
“Non-animal whey protein” is made in a process very similar to the production of corn ethanol. Corn is grown, processed into sugar and then fed to a microorganism programmed to eat the sugar and secrete a protein. Then, the protein is chemically separated from the microbe, likely with toxins like hexane.
This an energy-intensive, hyper-industrial process that is grossly inefficient. To make a gallon of ethanol, it takes more than 26 pounds of corn!
The process to harvest and produce corn-based ethanol creates more greenhouse gas emissions than normal gasoline.
Even if the feed ratio of precision fermentation were 1 to 1, as some claim (seems impossible), synthetic “milk” would still be much less efficient than cow’s milk.
Grain-fed cows eat no more than 3 pounds of corn per gallon of milk, and grass-fed cows don’t eat any! (Three pounds of corn is equal to a half-gallon of milk, using a recipe measurement converter.)
100% grass-fed organic dairy doesn’t require growing corn for cows. Well-managed pastures sequester more greenhouse gasses than the cows grazing it emit.
Real milk can be carbon negative. Industrially produced synbio milk will always have a carbon footprint.
The climate benefit of veganism is that food is grown directly for people. Growing food to feed to animals is inherently inefficient. Growing food to feed fungus in a factory isn’t any better.
TAKE ACTION: Ban New GMO Frankenfoods Made with Synthetic Biology (a.k.a “Precision Fermentation”)

MIND & BODY
The Nature Cure: How Time Outdoors Transforms Our Memory, Imagination and Logic
Sam Pyrah writes for The Guardian:
“You are probably aware of studies showing that green (vegetated) and blue (moving water) environments are associated with a reduction in stress, improved mood, more positive emotions and decreases in anxiety and rumination. But there is growing evidence that nature exposure also benefits cognitive function – all the processes involved in gaining knowledge and understanding, including perception, memory, reasoning, judgment, imagination and problem-solving. One study found that after just 40 seconds of looking out at a green roof, subjects made fewer mistakes in a test than when they looked at a concrete one.
What might be going on here? According to the biophilia hypothesis popularized by the American sociobiologist EO Wilson, humans function better in natural environments because our brains and bodies evolved in, and with, nature. ‘Biophilia makes a lot of sense,’ says Dr David Strayer, a cognitive neuroscientist who heads the Applied Cognition Laboratory at the University of Utah. “As hunter-gatherers, those who were most attuned to the natural environment were the most likely to survive. But then we built all this infrastructure. We are trying to use the hunter-gatherer brain to live in the highly stressful and demanding modern world.’”

DR. JOSEPH MERCOLA
Why You Should Take Your Apple Cider Vinegar at Night
Analysis by Dr. Joseph Mercola:
STORY AT-A-GLANCE
- NBC News reported that half the U.S. population suffers from either high blood sugar or full-blown diabetes, and half of them don’t even realize it
- Eleven study subjects had a little apple cider vinegar with cheese as a bedtime snack and woke up the next day with significantly lowered blood glucose levels
- Apple cider vinegar is useful for a number of health-related conditions, such as balancing your pH, increasing your good gut bacteria and helping to control your weight
- ACV uses are various and unexpected; its antibacterial effects help cure athlete’s foot and heal wounds, the acetic acid helps tone your skin and treat dandruff and the same compounds make it useful for cleaning around the house
Learn how ACV is beneficial for many different types of health issues

USDA WATCH
Small Meat Processors Say USDA Measures Don’t Address Industry’s Root Problems
John McCracken, Investigate Midwest:
“Over the past two decades, Greg Gunthorp carved out a niche operating a small meat processing plant in northern Indiana. He sold several kinds of meat to chic Chicago and Indianapolis restaurants and to Chicago O’Hare International Airport, he said. He also sold direct to consumers.
But selling in grocery stores was not an option, as the largest meatpackers often have those contracts. In his circumstances, he found it difficult to compete in the chicken industry, and he recently stopped raising and slaughtering the bird.
“In an extremely concentrated marketplace,” he said, “it’s difficult for a small processor — especially a plant that slaughters — to find a sweet spot somewhere to fit long term.”
Burdened with relatively higher operating costs than the largest meat processors, small meatpacking plants are struggling to survive — even with $1 billion in federal grants available to them.
In an industry in which four companies — Tyson Foods, JBS, Smithfield and Marfrig — control most of the meat market, small slaughterhouses are struggling to compete. The Biden administration has tried to address the concentration, including offering grants to help small processors expand. But it’s not enough for many small processors that face proportionately higher operating expenses than the industry giants, according to interviews with small processors and experts.
Read about how, even with USDA grants, the root problems in the industry remain unaddressed
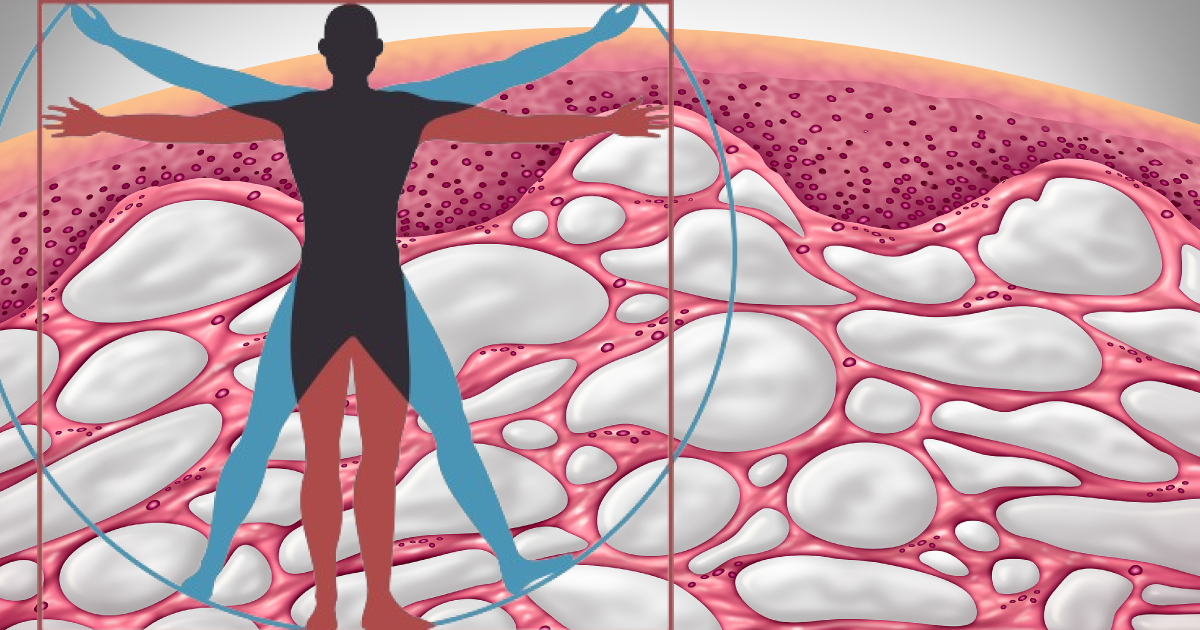
HEALTH SCIENCE
A “New” Part of the Human Body, the Interstitium
Jennifer Brandel writes for Orion:
“Here’s just a glimpse of what’s becoming known about it. The structure of the interstitium is fractal; it exhibits the same pattern at various scales. It’s unified. While scientists had seen glimpses of this mesh-like network before, they had not realized that it connected the entire body — just underneath the skin, and wrapping around organs, arteries, capillaries, veins, head to toes. It’s juicy. It moves four times more fluid through the body than the vascular system does. The fluid isn’t blood, it’s a clear and “pre-lymphatic” substance, carrying within it nutrients, information, and new kinds of cells that are only just being discovered. It’s also a conduit for cancer spread. Turns out that cancer cells moving through the interstitium’s channels are fast.
In short: it’s very important. And it’s wild that, although the interstitium can be seen with the naked eye during surgery, it wasn’t really noticed until now. There is an entire scientific revolution set to unfurl as more studies are peer-reviewed and more science books and classrooms integrate its existence into their cosmologies. We are at the beginning of it all.”
This essay is a companion piece to an episode of Radiolab, titled The Interstitium. You don’t need to have heard it for this essay to make sense, but listening to it will no doubt enrich your understanding.

LITTLE BYTES
Other Essential Reading and Videos for the Week
How Does Your Favorite Organic Dairy Brand Rate?
Over 100 Places to Buy Heirloom, Organic, and Non-GMO Seeds
US Lab Is Linked to COVID Virus, Before Outbreak
Big Promises To Indigenous Groups From New Global Nature Fund — But Will It Deliver?
Flavor Packed Ginger Syrup Recipe
The Big Pineapple Pesticide Problem
Soil Tasting: The Pleasures and Benefits of Healthy Soil
Free Entrance Days in the National Parks
Surprising Ways To Use Hydrogen Peroxide In Your Home
A Slow Food Academy to Protect Indigenous Peoples’ Food Systems
How to Protect Plants from Winter Elements
Nearly Half of the World’s Flowering Plants Face the Threat of Extinction, Study Says
How to Live Completely Off Grid Without Debt




